Kicking off with How Blockchain Technology Ensures Crypto Security, this sets the stage for an exciting exploration of blockchain’s role in safeguarding cryptocurrencies.
Blockchain technology, cryptographic hash functions, decentralization, smart contracts, and immutable ledgers all play crucial roles in ensuring the security of digital assets.
Overview of Blockchain Technology
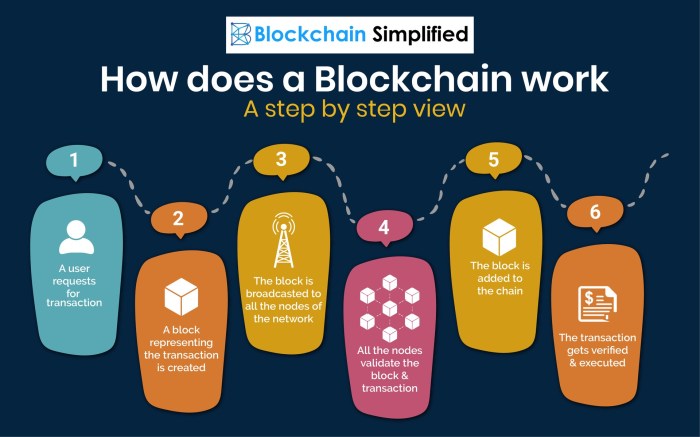
Blockchain technology is a decentralized system that enables the secure transfer of digital assets without the need for a central authority. It works by creating a chain of blocks that contain transaction data, which is cryptographically linked and stored across a network of computers.
Popular Blockchains in the Crypto Space, How Blockchain Technology Ensures Crypto Security
- Bitcoin: The first and most well-known blockchain, used for peer-to-peer transactions and store of value.
- Ethereum: Known for its smart contract capabilities, allowing developers to build decentralized applications.
- Ripple: Focuses on enabling fast and low-cost cross-border payments through its XRP cryptocurrency.
Role of Blockchain in Ensuring Security for Cryptocurrencies
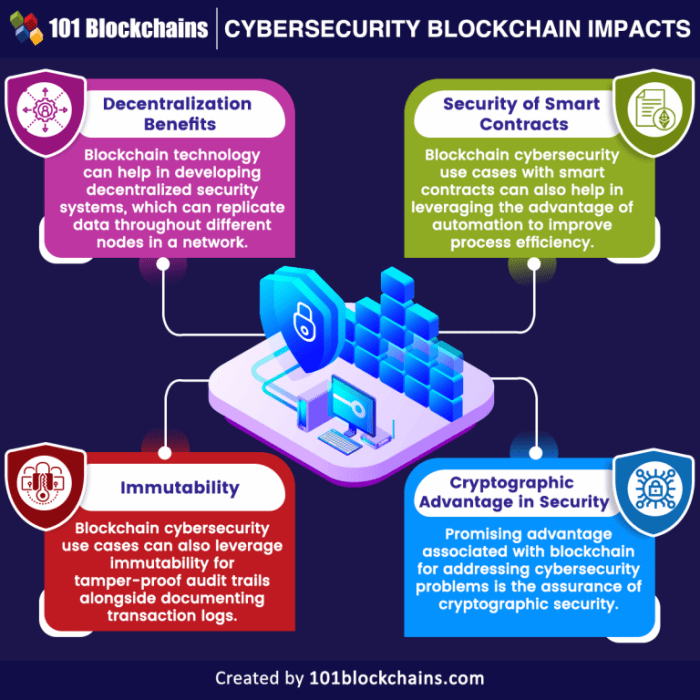
Blockchain technology ensures security for cryptocurrencies through its decentralized and immutable nature. Transactions recorded on the blockchain are transparent and cannot be altered once confirmed, providing a high level of security against fraud and tampering. Additionally, the use of cryptography in blockchain technology helps protect user data and ensures the integrity of the network.
Cryptographic Hash Functions
Cryptographic hash functions play a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of blockchain technology. These functions are algorithms that take an input (or message) and produce a fixed-size string of characters, which is a unique representation of the original data.
The importance of hash functions in securing crypto transactions lies in their ability to create a digital fingerprint of the data being stored in each block of the blockchain. This fingerprint, also known as the hash, is unique to each block and is used to verify the authenticity of the data. Any alteration to the data will result in a completely different hash, making it easy to detect any tampering.
Examples of Cryptographic Hash Functions:
- SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256): This is one of the most widely used cryptographic hash functions in blockchain networks, including Bitcoin. It generates a 256-bit hash value.
- RIPEMD (RACE Integrity Primitives Evaluation Message Digest): Another popular hash function used in blockchain technology, known for its ability to produce a shorter hash value compared to SHA-256.
- Keccak (SHA-3): A newer addition to the cryptographic hash function family, Keccak was chosen as the winner of the NIST hash function competition and is considered secure and efficient for blockchain applications.
Decentralization and Consensus Mechanisms

Decentralization plays a crucial role in ensuring the security of cryptocurrencies by distributing control among a network of nodes rather than relying on a central authority. This eliminates the risk of a single point of failure and makes it more resistant to hacks or manipulation.
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
- Proof of Work (PoW): In PoW, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This process requires a significant amount of computational power and energy, making it secure but resource-intensive.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): In PoS, validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. This eliminates the need for mining and reduces energy consumption, making it more environmentally friendly.
Decentralization ensures that no single entity can control the entire network, making it more secure and resistant to attacks.
Consensus and Security
- Consensus mechanisms like PoW and PoS help maintain the integrity of the blockchain by ensuring that all nodes agree on the validity of transactions.
- Decentralization and consensus work together to prevent fraud, double-spending, and other malicious activities by requiring majority agreement before new transactions are added to the blockchain.
Smart Contracts and Security
Smart contracts play a crucial role in enhancing security within blockchain technology. These self-executing contracts are stored on the blockchain and automatically execute transactions when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of fraud.
Automating Trustless Transactions
Smart contracts automate trustless transactions by ensuring that the terms of the agreement are securely and transparently enforced without relying on a central authority. This eliminates the need for trust between parties, as the code itself dictates the execution of the contract.
- Example: In a real estate transaction, a smart contract can be used to automatically transfer ownership of a property to the buyer once the payment has been made. This eliminates the risk of fraud or disputes, as the contract is executed only when the conditions are met.
Security Vulnerabilities and Mitigation
While smart contracts enhance security, they are not immune to vulnerabilities. One common issue is the presence of bugs or coding errors that can be exploited by malicious actors. To mitigate these risks, developers can follow best practices such as code audits, testing, and incorporating security mechanisms like multi-signature requirements.
- Example: The infamous DAO hack in 2016 exploited a vulnerability in a smart contract, resulting in the theft of millions of dollars worth of Ethereum. This incident highlighted the importance of thorough code review and security measures in smart contract development.
Immutable Ledger and Transparency: How Blockchain Technology Ensures Crypto Security
Blockchain technology utilizes an immutable ledger, meaning that once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature ensures the integrity and security of the data stored on the blockchain.
Transparency in blockchain transactions refers to the ability of anyone to view the entire history of transactions on the blockchain. This transparency adds a layer of security to cryptocurrencies as it allows all participants to verify the validity of transactions and prevent any fraudulent activity.
Impact of Immutable Ledger
- The immutable ledger in blockchain prevents unauthorized alterations to transaction records, making it extremely difficult for hackers to manipulate data.
- This feature has significantly reduced the risk of fraud in the crypto space, as every transaction is securely recorded and cannot be tampered with.
- Examples like the transparency of the Bitcoin blockchain have helped in identifying and stopping fraudulent activities, ensuring the security of the network.